James Sacchettini's laboratory at Texas A&M University recently solved several structures, including the structure of Rsr, an ortholog of the antigenic Ro protein. Ro proteins are a class of antigenic ribonucleo-proteins associated with rheumatic autoimmune diseases in humans. Ro is suggested to play a role in RNA quality control and has also been implicated in cell survival following UV damage. The 1.9-Å crystal structure of this prokaryotic ortholog, Rsr from D. raiodurans, was determined using GM/CA-CAT beamtime. It is composed of an N-terminal domain consisting of 18 α-helices and a C-terminal domain of a β-sheet (blue) sandwiched between sets of helices. Residues in the C-terminal domain coordinate a calcium ion (yellow).
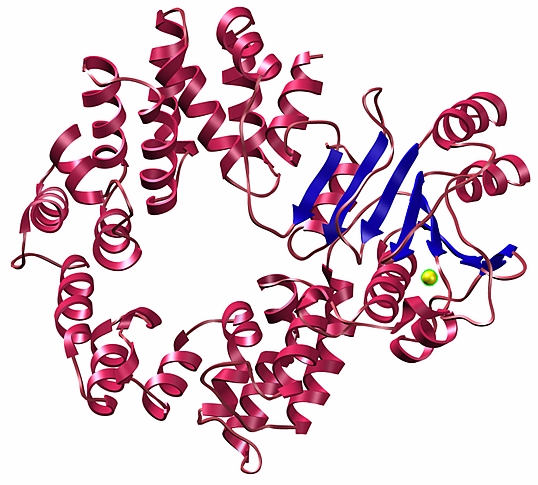 |
Figure: 1.9-Å crystal structure of D. radiodurans Rsr. |
Citation:
Ramesh, A, Savva, CG, Holzenburg, A, Sacchettini, JC. Crystal Structure of
Rsr, an Ortholog of the Antigenic Ro Protein, Links Conformational
Flexibility to RNA Binding Activity, J. Biol. Chem. 282 (20), 14960-14967
(2007). DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M611163200.