 |
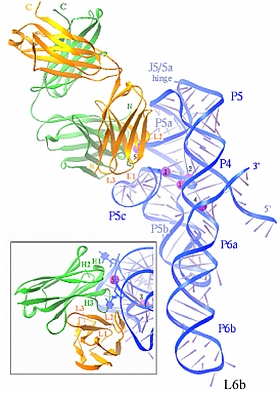
Figure: Ribbon representation of FAB2-ΔC209 complex. The FAB2 heavy and light chains are colored in green and orange, respectively. The RNA backbone is shown as a blue ribbon and the RNA bases are shown as cones. Protein and RNA termini, FAB2 CDRs and RNA stems are labeled. Five cations (labeled 1-5) bound to RNA are shown as small magenta spheres. The insert shows a perpendicular view of the RNA-protein interface. CDRs H1, H2 and H3 for the heavy chain and L1, L2, L3 for the light chain are labeled. Two bulged-out uridines, U130 and U179, which are present at the P5a/P5c interface and involved in the interaction with FAB2, are shown in ball-and-stick mode and colored blue. |
The groups of Kossiakoff, Piccarilli, and Koide provided a highlight on using Fabs to facilitate RNA structural work. Antibodies that bind protein antigens are indispensable in biochemical research and modern medicine, but knowledge of RNA-binding antibodies and their application in the ever-growing RNA field is lacking. The authors developed a robust approach using a synthetic phage-display library to select specific antigen-binding fragments (Fabs) targeting a large functional RNA. Using data collected at GM/CA-CAT, SBC-CAT, and SER-CAT, they solved the crystal structure of the first Fab-RNA complex at 1.95-Å resolution. The crystal structure reveals that the Fab achieves specific RNA binding on a shallow surface with complementarity-determining region (CDR) sequence diversity, length variability, and main-chain conformational plasticity (Fig. 12). The Fab-RNA interface also differs significantly from Fab-protein interfaces in amino acid composition and light-chain participation. The utility in phasing and in crystal-contact formation suggests that Fabs can serve as potentially valuable crystal chaperones for RNA. These findings yield valuable insights for engineering of Fabs as RNA-binding modules and facilitate further development of Fabs as possible therapeutic drugs and biochemical tools to explore RNA biology.
Citation:
Ye, J-D, Tereshko, V, Frederiksen, JK, Koide, A, Fellouse, FA, Sidhu, SS,
Koide, S, Kossiakoff, AA, Piccirilli, JA, Synthetic antibodies for specific
recognition and crystallization of structured RNA, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
105 (1), 82-87 (2008). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0709082105.