Harry Noller's group at the University of California at Santa Cruz published very challenging work on the structural basis for translation termination on the 70S ribosome. At the termination of protein synthesis on the ribosome, a stop codon on the messenger RNA signals peptide release. The three-base sequence of the stop codon is recognized by a type I release factor, which in turn induces hydrolysis of the peptidyl-tRNA ester linkage, releasing the completed protein. Using X-ray diffraction data collected at GM/CA-CAT's beamline 23 ID-D, after preliminary screening at SSRL, researchers at UC Santa Cruz determined the structure of an RF1-70S ribosome termination complex at 3.2 Å resolution. The structure explains stop codon recognition, directly implicates the release factor in the esterase reaction, and suggests how recognition of a stop codon triggers peptidyl-tRNA hydrolysis some 80 Å away.
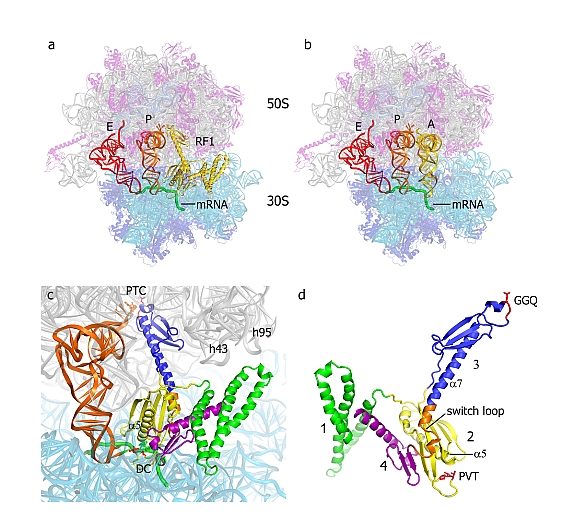 |
Figure: Structure of RF1 in the 70S translation termination complex. (A) Positions of RF1 (yellow), P-site tRNA (orange), E-site tRNA (red) and a mRNA (green) bound to the 70S ribosome [23S rRNA (gray), 5S rRNA (light blue), 16S rRNA (cyan), 50S proteins (magenta) and 30S proteins (dark blue)]. (B) The position of A-site tRNA (yellow) in a corresponding elongation complex is similar to that of domains 2, 3 and 4 of RF1. (C) Orientation of RF1 in the A site of the 70S ribosome, along with the P-site tRNA (orange). The peptidyl transferase center (PTC), decoding center (DC) and helices h43 (the GTPase-associated center) and h95 (the sarcin-ricin loop) of 23S rRNA are indicated. (D) The structure of RF1 in its ribosome-bound conformation. [ Figure reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Nature, 2008] |
Citation:
Laurberg, M, Asahara, H, Korostelev, A, Zhu, J, Trakhanov, S, Noller, HF.
Structural basis for translation termination on the 70S ribosome, Nature 454,
852-857 (2008). DOI: 10.1038/nature07115.