 |
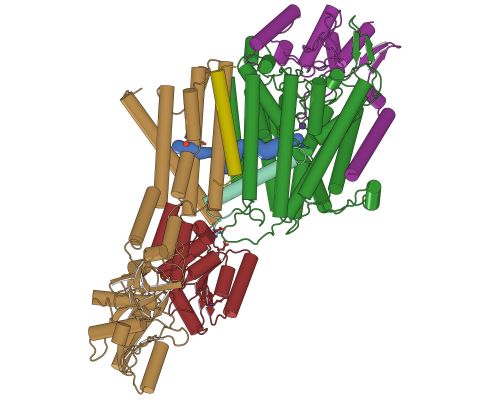
Figure: The structure of KdpFABC shown with green KdpA, brown/red KdpB, purple KdpC and olive KdpF. |
The group of David Stokes at New York University published the structure of an intriguing membrane-spanning ion pump. In order to survive at very low K+ concentrations, bacteria have evolved the high-affinity, inducible Kdp system that functions as a primary active transporter. KdpFABC is a heterotetrameric membrane complex that uses ATP to pump K+ into the cell in an unprecedented partnership between a channel-like subunit (KdpA) and a pump-like subunit (KdpB). KdpA belongs to the superfamily of K+ transporters and KdpB is a P-type ATPase, but both subunits have been repurposed in the Kdp complex. KdpB is a P-type ATPase that does not pump, but rather uses ATP-driven conformational changes to control KdpA. KdpA has been adapted to move ions against an electro-chemical potential. The structure hints at how this process works. In particular, a kinked helix (cyan) in KdpA is coupled to the KdpB catalytic domain (dark red), which may control the cytoplasmic gate to the K+ transport pathway. A tunnel (blue) buried within the membrane domain links the KdpA selectivity filter (occupied by K+) and the KdpB canonical cation binding site (occupied by a water molecule). Stokes and colleagues have proposed that charge is transferred through this tunnel by a water wire, thus coupling ion binding within KdpA to ATP hydrolysis by KdpB and inducing conformational changes that lead to the translocation of K+ across the membrane.
Citation: Huang, C-S, Pedersen, BP, Stokes, DL Crystal structure of the potassium-importing KdpFABC membrane complex, Nature 546, 681-685 (2017). DOI: 10.1038/nature22970