A team lead by Dr. Xiaojiang Chen at the University of Southern California have discovered a new mechanism that regulates the enzymatic activity of APOBEC3G (A3G), a protein that plays a vital role in the body's defense against viruses like HIV by editing viral DNA. A3G belongs to a family of enzymes that can mutate DNA by converting cytidine (C) to uridine (U), a process that can restrict viral replication or cause cancer. In this study, scientists found that A3G's editing activity is enhanced by specific sequences, known as AA, positioned near the editing site. These motifs help guide A3G to its target, boosting its efficiency. This process involves A3G's non-catalytic domain, which captures these sequences, allowing it to locate and edit DNA more effectively. The research team also visualized the A3G protein bound to DNA through high-resolution structural analysis, revealing the interactions between A3G and these DNA motifs. This new understanding of A3G mechanism not only explains how it functions in antiviral immunity but also provides insights into how A3G may contribute to DNA mutations associated with cancer when misregulated. By clarifying the cooperative role of A3G's two domains, this discovery paves the way for potential therapeutic approaches targeting A3G's activity in viral infections and cancer.
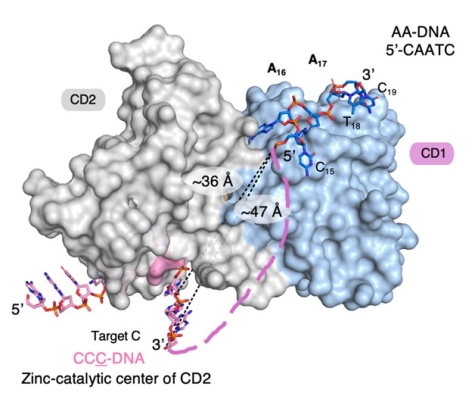 |
Figure: DNA substrate captured by CD1 via AA-motif recognition to dictate the CC-motif deamination by the catalytic CD2 of A3G |
Citation: Yang, H, Pacheco, J, Kim, K, Bokani, A, Ito, F, Ebrahimi, D, Chen, XS, "Molecular mechanism for regulating APOBEC3G DNA editing function by the non-catalytic domain," Nat. Commun. 15, 8773 (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-52671-1